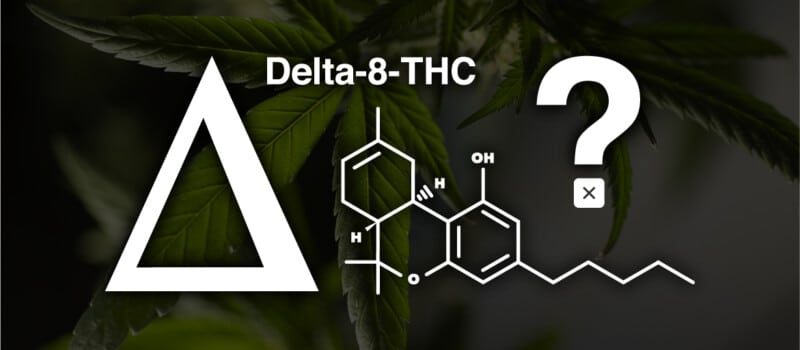
HHC is a synthetic cannabinoid that is structurally related to THC but has different effects and potency. It’s more resistent to heat but weaker than THC because it lacks a double bond in the 9th carbon chain position. HHC is supposedly better at binding to CB receptors.
The Chemistry of HHC
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a naturally occurring cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. Its molecular structure is composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms arranged in a specific configuration. Chemically, HHC is classified as a bicyclic terpene derivative.
Unlike other well-known cannabinoids such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), HHC possesses a unique molecular arrangement. It is characterized by a six-membered carbon ring fused with another six-membered carbon ring, along with additional substituents. This distinctive structure distinguishes HHC from other cannabinoids and contributes to its potential effects and interactions within the body.
Similarities and differences with other cannabinoids
While HHC shares some similarities with other cannabinoids found in cannabis, it also exhibits notable differences. One of the primary distinctions lies in its psychoactive properties. HHC is believed to have a lower potency in inducing psychoactive effects compared to THC, which is the primary psychoactive component of cannabis.
Moreover, HHC has been found to interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), much like other cannabinoids. The ECS is a complex network of receptors and molecules distributed throughout the body, responsible for regulating various physiological processes. HHC’s interaction with the ECS may contribute to its potential therapeutic effects.
Extraction and synthesis methods
The extraction of HHC from cannabis plants can be achieved through various methods. One common approach involves using solvents like ethanol or supercritical carbon dioxide (CO2) to isolate the compound from the plant material. After extraction, purification techniques are employed to obtain a highly concentrated and pure form of HHC.
In addition to extraction from the plant, researchers have also explored the synthesis of HHC in the laboratory. Synthetic production allows for better control over the purity and concentration of the compound, enabling more consistent research and experimentation.
The development of efficient and scalable extraction and synthesis methods for HHC is crucial for furthering our understanding of its properties and potential applications.
As research on HHC progresses, a deeper understanding of its chemistry will contribute to unraveling its mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic uses.
Further exploration of its molecular structure and interactions with the endocannabinoid system will shed light on the unique properties of HHC and its potential benefits.
Pharmacology and Potential Effects
One of the key aspects of HHC pharmacology is its interaction with the endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body, regulating such processes as:
- Sensation of pain;
- Mood;
- Appetite;
- Immune function.
HHC has been found to bind to cannabinoid receptors, mainly CB1 and CB2, which are located throughout the body and central nervous system.
Affinity for cannabinoid receptors
HHC has different affinities for cannabinoid receptors, which affects its potential effects. Although it binds to the same receptors as other cannabinoids, its affinity and activity may differ. This unique binding profile may contribute to different physiological responses and therapeutic outcomes.
Psychoactive and therapeutic potential
Although HCQ is a cannabinoid, it is generally believed to have less ability to induce psychoactive effects compared to THC. This could make it a potentially desirable option for people seeking the therapeutic benefits of cannabis without experiencing strong psychoactive effects.
As for its therapeutic potential, research on HHC is still in its early stages. Preliminary studies suggest that HHC may have analgesic (analgesic), anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. It is thought to modulate the release of neurotransmitters and affect signaling pathways involved in pain perception, inflammation and neurological disorders.
Comparison with other cannabinoids
When comparing HCQ to other cannabinoids such as THC and CBD, important differences arise. THC is known for its psychoactive effects, while CBD is not intoxicating and has gained popularity for its potential therapeutic properties. HHC is somewhere in the middle, having a milder psychoactive profile than THC, but potentially a different therapeutic effect than CBD.
It is worth noting that research on HHC is limited compared to THC and CBD. Therefore, further studies are needed to explore its full range of effects, safety profile, and potential interactions with other cannabinoids and medications.
Continued research will allow us to understand its mechanisms of action, efficacy, and safety, potentially opening the door to new treatment options and expanding our understanding of cannabinoid pharmacology.
Pharmacology and Potential Effects
One of the key aspects of HHC’s pharmacology lies in its interaction with the endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis within the body, regulating processes such as pain sensation, mood, appetite, and immune function. HHC has been found to bind to cannabinoid receptors, primarily CB1 and CB2, which are located throughout the body and central nervous system.
Study of potential therapeutic use
Research into the potential therapeutic uses of HHC includes:
- Effects on inflammation;
- Neuroprotection;
- Epilepsy;
- Multiple Sclerosis.
It is important to note that these potential therapeutic applications are based on early studies, and further research is needed to confirm and extend these preliminary results.
Psychoactive and therapeutic potential
Although HHC is a cannabinoid, it is generally believed to possess a lower potency in inducing psychoactive effects compared to THC. This may make it a potentially desirable option for individuals seeking the therapeutic benefits of cannabis without experiencing intense psychoactive effects.
Regarding its therapeutic potential, research on HHC is still in its early stages. Preliminary studies suggest that HHC may have analgesic (pain-relieving), anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties.
It is believed to modulate the release of neurotransmitters and influence signaling pathways involved in pain perception, inflammation, and neurological disorders. However, further research is needed to fully understand its therapeutic efficacy and potential applications.
Future Directions and Challenges
As the understanding of HHC continues to evolve, there are several areas of research that hold promise for further exploration:
- Mechanisms of action;
- Clinical trials;
- Comparative studies.
Understanding the unique properties of HHC will contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the cannabis plant and its therapeutic potential.
Clinical trials and evidence-based studies
The successful completion of rigorous clinical trials is essential for establishing HHC as a safe and effective therapeutic option. These studies can provide robust evidence of its efficacy in specific medical conditions and help guide healthcare professionals in prescribing guidelines.
Potential limitations and hurdles
There are several challenges and considerations that researchers and regulators may face when exploring HHC:
Regulatory framework
The legal and regulatory landscape surrounding HHC and other cannabinoids is complex and varies across different jurisdictions. Developing a clear and consistent regulatory framework for HHC will be crucial for its safe and responsible use.
Quality control and standardization
Ensuring consistent quality and potency of HHC products is essential for both research and clinical applications. Establishing standardized protocols for extraction, synthesis, and quality control will help maintain product consistency and reliability.
Safety and side effects
Conducting comprehensive safety studies and monitoring potential side effects will be critical in understanding the risk-benefit profile of HHC. This includes assessing any potential interactions with other medications and evaluating its long-term effects.
Implications for medical and recreational cannabis use
The continued exploration of HHC’s properties and potential therapeutic applications will have broader implications for the medical and recreational cannabis industry. Understanding its distinct effects and therapeutic potential can inform the development of new cannabis-based medications and influence regulations surrounding cannabis use.
Further research on HHC is warranted to unlock its full potential. Overcoming the challenges and pursuing evidence-based studies will be crucial in establishing its efficacy, safety, and optimal use in various medical conditions. By addressing these future directions and challenges, scientists and policymakers can pave the way for the responsible integration of HHC into healthcare practices and potentially expand the therapeutic options available to patients.
Implications for Medical and Recreational Cannabis Use
The continued exploration of HHC’s properties and potential therapeutic applications will have broader implications for the medical and recreational cannabis industry. Understanding its distinct effects and therapeutic potential can inform the development of new cannabis-based medications and influence regulations surrounding cannabis use.
Overcoming the challenges and pursuing evidence-based studies will be crucial in establishing its efficacy, safety, and optimal use in various medical conditions.
The Final Word
Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is an intriguing and understudied compound within the vast array of cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. As scientific understanding and interest in cannabis research continue to grow, investigating HHC’s unique properties and potential applications holds promise for advancing our knowledge of the plant’s therapeutic and recreational effects.
Further exploration of HHC could contribute to the development of novel treatments and inform regulatory decisions surrounding cannabis use. With ongoing research, HHC might emerge as a significant player in the world of cannabis science, benefiting both medical professionals and individuals seeking alternative therapeutic options.