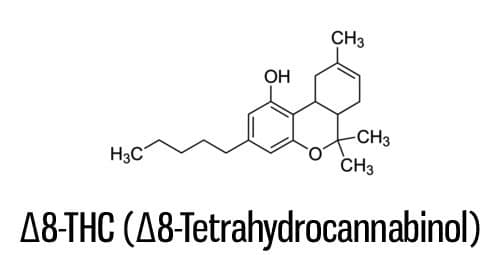
If delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) sounds familiar, it’s probably because the most well-known cannabinoid is delta-9-THC. As you may have guessed, the two compounds aren’t vastly different; in fact, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) defines delta-8-THC as “an analogue of THC.” However, that doesn’t go to say the two compounds are identical.
According to the NCI, delta-8-THC has “antiemetic, anxiolytic, appetite-stimulating, analgesic, and neuroprotective properties.”
How Strong is Delta-8-THC
As far as potency goes, the difference between delta-8-THC and delta-9-THC has been estimated at a ratio of 2:3. [1]
Anti-Emetic Properties
One of the most pronounced applications of delta-8-THC is its anti-emetic properties, which alleviate nausea. This ability clearly comes as a godsend for cancer patients who deal with nausea daily, especially as a result of chemotherapy.
A testament to delta-8-THC’s anti-emetic properties is a 1995 study on 8 children with cancer (ages 3 to 13) in which vomiting “was completely prevented” thanks to the cannabinoid. [2]
Appetite Stimulant
Being a true analogue of THC, delta-8-THC also might make you rummage through your fridge in the middle of the night like a wolverine. In fact, despite being less potent otherwise, as far as the munchies in mice go, delta-8-THC summons them even more powerfully than delta-9-THC. [3]
Cancer
While very little exploration of delta-8-THC’s potential to battle cancer has been undertaken, the limited research has actually been quite promising.
All the way back in 1975, a study on mice with lung cancer found that 20-day treatment with delta-8-THC reduced their tumour size; the cannabinoid increased life span by roughly 25% at 200mg/kg. [4]
Memory
Delta-8-THC has displayed neuroprotective properties, such as increasing the acetylcholine levels in the brains of mice. [5] Considering that Alzheimer’s is accompanied by low levels of acetylcholine, delta-8-THC’s neuroprotective properties could turn out to be highly applicable to this disease.
Limitations
Unlike delta-9-THC, delta-8-THC is found in significantly smaller quantities in cannabis, the difference being reminiscent of the way scientists compare the sizes of planets. Delta-8-THC’s amount in a cannabis cultivar may fall into in the ballpark of under 1% or even much, much less.
With that being said, companies like Oleum Extracts and FarmaceuticalRx are already focusing energy on the obscure cannabinoid, and with advancements in cannabis extraction and the compound’s potential, no doubt more will follow.
References:
- Hollister LE and Gillespie HK. “Delta‐8‐ and Delta‐9‐Tetrahydrocannabinol; Comparison in Man by Oral and Intravenous Administration, Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics.” Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics, vol.14, no.3, 1973. Journal Impact Factor = 7.266; Times Cited = 64 (GoogleScholar)
- Abrahamov A, et al. “An Efficient New Cannabinoid Antiemetic in Pediatric Oncology.” Life Sci,56, no.23-24, 1995, pp.2097-102. Journal Impact Factor =3.488; Times Cited = 188 (GoogleScholar)
- Avraham Y, et al. “Very Low Doses of Delta 8-THC Increase Food Consumption and Alter Neurotransmitter Levels Following Weight Loss.” Pharmacol Biochem Behav, vol.77, no.4, 2004, pp.675-84. Journal Impact Factor = 2.781; Times Cited = 34 (ResearchGate)
- Munson AE, et al. “Antineoplastic Activity of Cannabinoids.” Journal of the National Cancer Institute, vol.55, no.3, 1975, pp. 597–602. Journal Impact Factor = 12.589; Times Cited = 288 (GoogleScholar)
- Tripathi HL, et al. “Effects of Cannabinoids on Levels of Acetylcholine and Choline and on Turnover Rate of Acetylcholine in Various Regions of the Mouse Brain.” Alcohol Drug Res, vol.7, no.5-6, 1987, pp.525-32. Journal Impact Factor = N/A; Times Cited = 15 (ResearchGate)
Image Credits: Sespe Creek